Physical generative AI
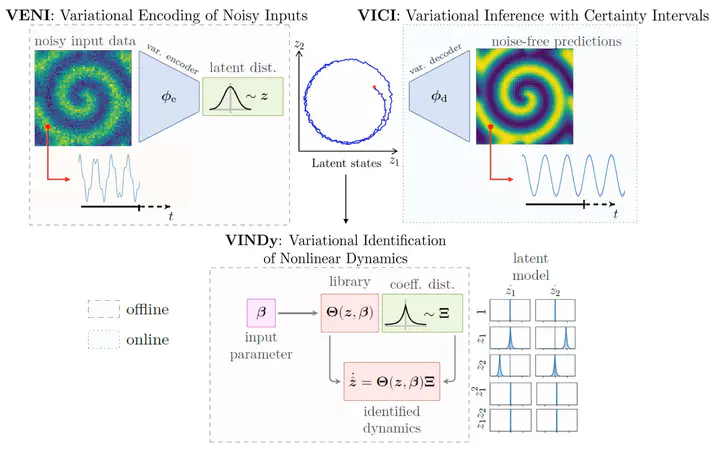
In this project we develop a data-driven, non-intrusive framework for building generative reduced-order models (ROMs) where the latent variables and dynamics are identified in an interpretable manner and uncertainty is quantified. Starting from a limited amount of high-dimensional, noisy data the proposed framework constructs an efficient ROM by leveraging variational autoencoders for dimensionality reduction along with a dynamical system identification technique named VINDy (Variational Identification of Nonlinear Dynamics). In detail, the method consists of Variational Encoding of Noisy Inputs (VENI) to identify the distribution of reduced coordinates. Simultaneously, we learn the distribution of the coefficients of a pre-determined set of candidate functions by VINDy. Once trained offline, the identified model can be queried for new parameter instances and new initial conditions to compute the corresponding full-time solutions. The probabilistic setup enables uncertainty quantification as the online testing consists of Variational Inference naturally providing Certainty Intervals (VICI). In this project we showcase the performance of the overall method - named VENI, VINDy, VICI - on partial differental equations (PDEs) benchmarks including structural mechanics and fluid dynamics.
Contributors: Paolo Conti, Jonas Kneifl.
